RESTRICTION ENZYMES
● In the year `color{Violet}"1963"`, the `color{Violet}"two enzymes"` responsible for restricting the growth of `color{Violet}"bacteriophage"` in Escherichia coli were isolated.
● One of these `color{Violet}"added methyl groups"` to DNA, while the other `color{Violet}"cut DNA"`.
● The later was called `color{Brown}"restriction endonuclease"`.
● The `color{Brown}"first restriction endonuclease"`–`color{Violet}"Hind II"`, whose functioning depended on a specific DNA nucleotide sequence was isolated and characterised `color{Violet}"five years later"`.
● It was found that `color{Violet}"Hind II"` always cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognising a `color{Violet}"specific sequence"` of six base pairs.
● This `color{Violet}"specific base sequence"` is known as the `color{Brown}"recognition sequence"` for Hind II.
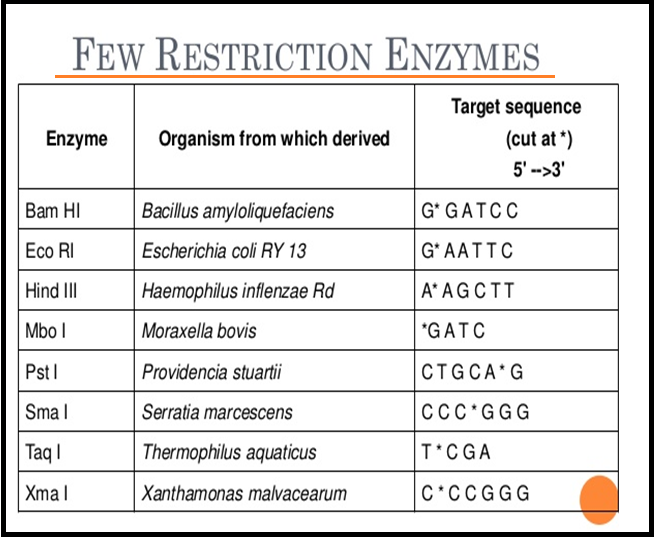
● Besides Hind II, today we know more than `color{Violet}"900 restriction enzymes"` that have been isolated from over `color{Violet}"230 strains of bacteria"` each of which recognise different recognition sequences

.
● The `color{Violet}"convention for naming"` these enzymes is the `color{Violet}"first letter"` of the name comes from the genes and the `color{Violet}"second two letters"` come from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they were isolated.
● `color{Brown}"E.g"`., `color{Violet}"EcoRI"` comes from `color{Violet}"Escherichia coli"` `color{Violet}"RY 13"`. In EcoRI, the letter ‘R’ is derived from the name of strain.
● `color{Violet}"Roman numbers"` following the names indicate the `color{Violet}"order"` in which the `color{Violet}"enzymes were isolated"` from that strain of bacteria.
● One of these `color{Violet}"added methyl groups"` to DNA, while the other `color{Violet}"cut DNA"`.
● The later was called `color{Brown}"restriction endonuclease"`.
● The `color{Brown}"first restriction endonuclease"`–`color{Violet}"Hind II"`, whose functioning depended on a specific DNA nucleotide sequence was isolated and characterised `color{Violet}"five years later"`.
● It was found that `color{Violet}"Hind II"` always cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognising a `color{Violet}"specific sequence"` of six base pairs.
● This `color{Violet}"specific base sequence"` is known as the `color{Brown}"recognition sequence"` for Hind II.
● Besides Hind II, today we know more than `color{Violet}"900 restriction enzymes"` that have been isolated from over `color{Violet}"230 strains of bacteria"` each of which recognise different recognition sequences

.
● The `color{Violet}"convention for naming"` these enzymes is the `color{Violet}"first letter"` of the name comes from the genes and the `color{Violet}"second two letters"` come from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they were isolated.
● `color{Brown}"E.g"`., `color{Violet}"EcoRI"` comes from `color{Violet}"Escherichia coli"` `color{Violet}"RY 13"`. In EcoRI, the letter ‘R’ is derived from the name of strain.
● `color{Violet}"Roman numbers"` following the names indicate the `color{Violet}"order"` in which the `color{Violet}"enzymes were isolated"` from that strain of bacteria.


